State 상태
State는 React 컴포넌트의 데이터를 말하며, 개발자가 정의하는 것으로 렌더링이나 데이터 흐름에 사용되는 값만을 State에 포함시켜야합니다.
또한, State는 특별한 값이 아닌 Javascript의 객체입니다.
State 정의
Class Component에서의 State
Class Component의 경우 State를 생성자에서 정의합니다. this.state 코드로 현재 컴포넌트의 State로 정의합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
// Class Component class LikeButton extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { // state를 생성자에서 정의 liked: false }; } ... }
Function Component에서의 State
Function Component의 경우 State를 useState Hook을 사용해서 정의합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
// Function Component import { useState } from "react"; function Example() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); // useState Hook 사용 return ( <div> <p>버튼을 {count}번 눌렀습니다.</p> // <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>클릭</button> </div> ); }
State 수정하기
State 값을 직접 변경하게 되면 React가 Component를 다시 렌더링 할 타이밍을 알아차리지 못합니다.
따라서, 반드시 setState 함수를 이용해 값을 변경해야합니다.
setState 함수를 호출할 때 React에게 다시 렌더링 하라는 요청을 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// Class Component
this.state = { name: "Inje" };
this.setState({ name: "Inje" });
// Function Component
import { useState } from "react";
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>버튼을 {count}번 눌렀습니다.</p>
<button onClick={setCount(count + 1)}>클릭</button>
</div>
);
}
Object, Array를 갖는 State 수정하기
객체나 배열을 값으로 갖는 State를 수정할 때는 새로운 객체나 배열을 생성하고 변경합니다.
예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
// 잘못된 방법 const [user, setUser] = useState({ name: "민수", grade: 1 }); setUser((current) => { // user의 grade가 변경되었지만 user의 내용을 담는 object 자체가 변경된 것은 아니다. current.grade = 2; return current; }); // 올바른 방법 const [user, setUser] = useState({ name: "민수", grade: 1 }); setUser((current) => { // 기존 user의 내용을 새로운 object에 담고 grade를 변경 const newUser = { ...current }; newUser.grade = 2; return newUser; });
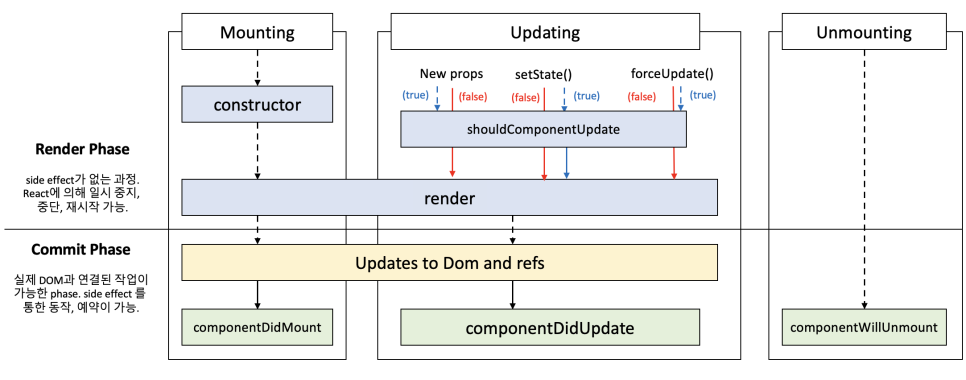
React의 생명주기 LifeCycle
생명주기란 App이 실행되고 종료되는 과정을 특정 시점 별로 나눠둔 것을 말합니다.
Mount 생성
Component가 실제 DOM에 삽입되는 것을 말합니다.
Update 업데이트
Component가 변화하는 것을 말합니다.
Unmount 삭제
Component가 DOM 상에서 제거되는 것을 말합니다.
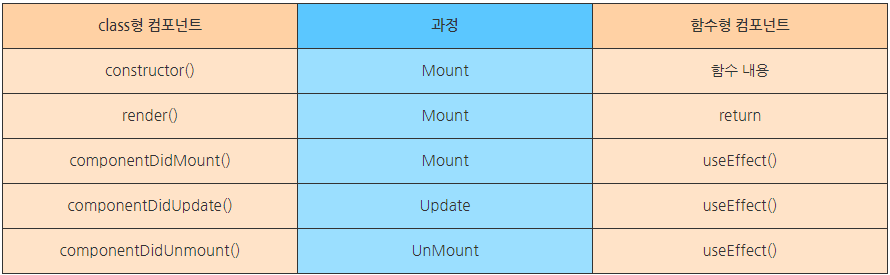
Class 컴포넌트
constructor() 함수
State를 초기화하는 메서드
render() 함수
클래스 컴포넌트에서 반드시 구현되어야 하는 렌더링 메서드
componentDidMount() 함수
컴포넌트가 마운트된 직후 호출되는 메서드
componentDidUpdate() 함수
컴포넌트가 업데이트된 직후 호출되는 메서드
componentWillUnmount() 함수
컴포넌트가 삭제되기 직전에 호출되는 메서드
componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, componentWillUnmount는 생명주기에 따라 호출되는 클래스 컴포넌트 함수로서 생명주기 함수입니다.
즉, 컴포넌트는 생명 주기를 갖으며, 시간에 따라 생성되고 업데이트되며 결국 삭제됩니다.
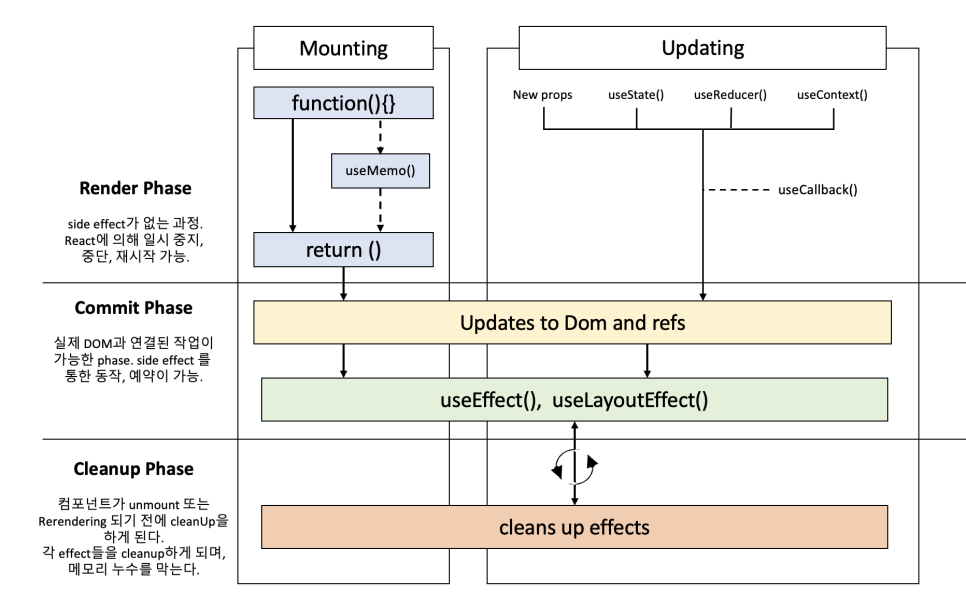
Function 컴포넌트
함수 컴포넌트에서는 클래스 컴포넌트에서 사용하던 메서드들이 일부 변경됩니다.
예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
// Class 컴포넌트 import React from "react"; class ClassExample extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { number: 0, }; this.handleNumber = this.handleNumber.bind(this); } handleNumber() { console.log(this.state.number); this.setState({ number: this.state.number + 1, }); } render() { return <button onClick={this.handleNumber}>버튼</button>; } } // 함수 컴포넌트 import React, { useCallback, useState } from "react"; const FunctionExample = () => { const [number, setNumber] = useState(0); const handleNumber = useCallback(() => { console.log(number); setNumber(number + 1); }); return <button onClick={handleNumber}>버튼</button>; };