자바스크립트의 반복문에 대해 알아보자.
for 문
for 문은 조건문이 false가 될 때까지 반복합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
let answer = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
answer += 1;
}
console.log(answer); // 3
장점
- 빠른 속도
- 변수 활용 가능
continue,break사용 가능
Array.prototype.forEach 메서드
forEach 메서드는 Callback을 배열에 있는 각 요소에 한 번씩 실행합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
arr.forEach((element, index) => {
console.log(`element : ${element}, index : ${index}`);
});
// element : 1, index : 0
// element : 2, index : 1
// element : 3, index : 2
장점
- 코드가 쉽고 간결함
- 성능 준수
- 매개변수 활용 가능
- 하지만, `continue`, `break` 사용 불가능
for…of 문
반복가능한 객체 (iterable)의 요소를 반복합니다.
요소의 값을 참조하며, 인덱스는 참조하지 못합니다.
- 반복가능한 객체
- Array, String, Map, Set 등
1
2
3
4
5
6
const str = "hello";
for (let s of str) {
console.log(s);
}
//출력결과: h, e, l, l, o
장점
- 코드가 간결함
- 성능 준수
continue,break사용 가능
for…in 문
객체의 열거 가능한 속성을 반복합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
// 객체 안에 들어있는 데이터만큼 반복문 수행
for (const key in obj) {
console.log(`${key}: ${obj[key]}`);
}
// "a: 1"
// 'b: 2"
// "c: 3"
장점
- 코드가 간결함
- 객체 접근 가능
continue,break사용 가능- 하지만, 성능이 다른 반복문에 비해 떨어짐
그 외
Array.prototype.map 메서드
배열의 각 요소에 대해 Callback을 실행하고 그 결과를 새 배열로 반환합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
const array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16]; // Pass a function to map const map1 = array1.map((x) => x * 2); console.log(map1); // Expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
Array.prototype.filter 메서드
배열의 각 요소에 대해 Callback을 실행하고 그 결과(Boolean)에 따라 필터링한 새 배열을 반환합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6
const words = ["spray", "elite", "exuberant", "destruction", "present"]; const result = words.filter((word) => word.length > 6); console.log(result); // Expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
Array.prototype.reduce 메서드
배열의 각 요소에 대해 Callback을 실행한 결과값을 새 배열로 반환합니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; // 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 const initialValue = 0; const sumWithInitial = array1.reduce( (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, initialValue ); console.log(sumWithInitial); // Expected output: 10
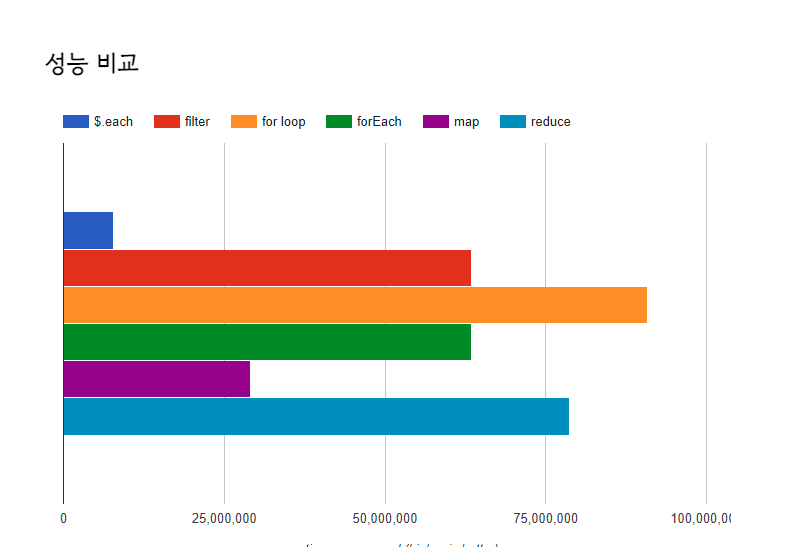
성능차이
평소에는 코드의 가독성을 고려해서 forEach를 사용하고 성능을 올리고 싶을 때 for문이나 optimized for문을 고려하면 좋을 것 같습니다.
map, reduce, filter 등은 해당 메서드의 기능을 목적으로 사용하면 좋을 것 같습니다.