Fetch API
Fetch API는 HTTP 요청과 응답 등을 Javascript에서 접근하고 조작할 수 있는 인터페이스를 제공합니다.
XMLHttpRequest 모듈과 비교해서 Fetch는 Promise 기반으로 구성되어 있어 더 간편하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
기본 구조
1
2
3
fetch(url, options)
.then((response) => console.log("response:", response))
.catch((error) => console.log("error:", error));
- fetch()는 첫 번째 인자로 url, 두 번째 인자로 option 객체를 받고, Promise 객체를 반환합니다.
- .then()에서 응답 객체를 받고, .catch()에서 에러를 받습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
fetch(url, {
method: 'post',
headers: {
"Content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"
},
body: 'foo=bar&lorem=ipsum'
})
.then((response) => console.log(response);)
.catch((error) => console.log(error));
- 두 번째 인자인 options 객체에 추가적인 데이터를 객체 변수에 저장해서 전달합니다.
Property
- method : HTTP 요청 방식 (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등)
- headers : 요청 헤더 정보
body : JSON 형태로 주고 받을 데이터
통신을 할 때는 String 형태의 JSON으로 보내야 하기 때문에 JSON.stringify()를 활용해서 JSON String으로 변환합니다.
- 그 외 : mode, cache 등
참고 글 : MDN사이트 - Fetch
fetch로 데이터 읽기
1
2
3
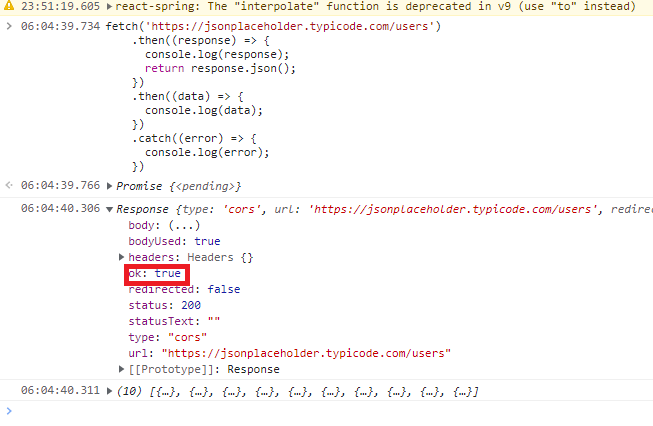
fetch(url, options)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => console.log(data));
- 위 코드는 JSON 파일을 가져와
console.log로 출력합니다. - fetch 함수는 Promise 객체를 반환합니다.
- 코드를 보면, then() 메서드를 체이닝하고 있습니다.
- 비동기로 처리된 fetch 함수의 결과 값이 들어오면 then 메서드를 실행합니다.
- 첫 번째
then()에서는 서버에서 보내준 응답의 본문을 추출합니다. - 두 번째
then()에서는 추출된 본문으로 작업합니다. (위의 예제에서는console.log)
첫 번째 then() 메서드
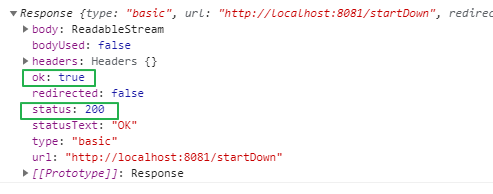
then() 메서드는 fetch()로 반환된 Promise 객체의 PromiseResult 값인 Response 객체를 보여줍니다.
Response 객체
response 객체는 HTTP 응답 전체를 나타내는 객체입니다.
Property
- response.body : ReadableStream의 내용
- response.headers : 응답 Headers와 관련된 객체
- response.ok : 응답의 HTTP 상태 코드가 200~299일 때 true (즉, 성공했는 지 여부를 나타내는 boolean)
- response.status : 응답의 HTTP 상태 코드
본문 추출 메서드
- response.json() : 응답을 JSON 형태로 파싱
- response.text() : 응답을 텍스트로 반환
- 그 외 : response.blob(), response.arrayBuffer() 등
참고 글 : mdn사이트 - response 객체
예외 처리
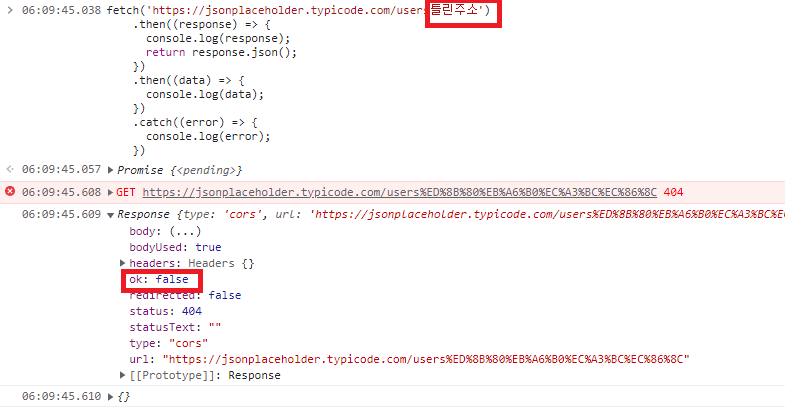
fetch()로 부터 반환된 Promise 객체는 상태 코드가 404, 500 등의 에러 코드여도 reject가 반환되지 않습니다.
즉, catch에서 error를 잡을 수 없습니다.
대신 reponse.ok가 false인 resolve가 반환됩니다.
네트워크 장애나 요청이 완료되지 못한 경우에는 reject가 반환됩니다.
두 번째 then() 메서드
첫 번째 then() 메서드에서 본문 추출 메서드로 반환된 Promise 객체에 다시 then() 메서드를 체이닝해 PromiseResult 값에 담긴 데이터를 사용합니다.
간단 예제
다음은 가상 데이터 api 사이트를 이용한 예제입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button onclick="getUser()">버튼</button> <h1>Authors</h1> <ul id="authors"></ul> <div id="userInfo"></div> <script> function getUser() { const ul = document.getElementById("authors"); const url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users"; fetch(url) .then((res) => { return res.json(); // 첫 번쨰 then() 에서 본문 추출 }) .then((data) => { // 두 번쨰 then() 부분에서 데이터 처리 let authors = data; authors.map((author) => { let li = document.createElement("li"); let name = document.createElement("h2"); let email = document.createElement("span"); name.innerHTML = `${author.name}`; email.innerHTML = `${author.email}`; li.appendChild(name); li.appendChild(email); ul.appendChild(li); }); }) .catch((err) => { console.log(err); }); } </script> </body> </html>
두 번째 then() 메서드에 data를 인자로 갖는 함수를 이용해 버튼을 누르면 응답 받은 데이터를 리스트로 보여주는 페이지입니다.
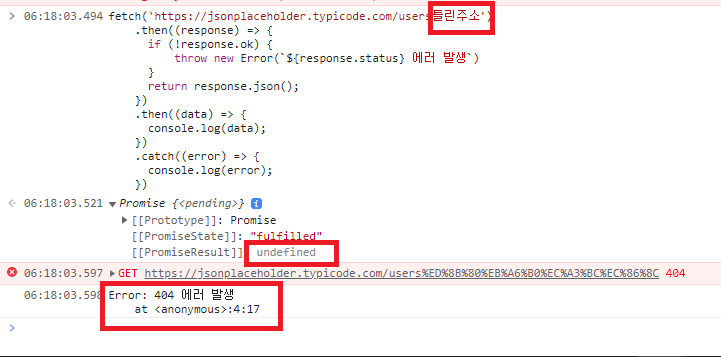
예외 처리
두 번째 then() 에서의 예외 처리는 데이터를 이용한 작업 과정에서 발생하는 예외를 처리합니다.- 간단 예제
POST 방식으로 회원가입 할 때 아이디가 이미 존재하는 경우 알림으로 알려주기
(서버의 API는 구현된 상태라고 가정하겠습니다.)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
fetch("API 주소", { method: "POST", body: JSON.stringify({ id: id, password: pw, }), }) .then((response) => response.json()) .then((data) => { if (data.message === "EXISTS") { alert("이미 있는 계정입니다."); } else { navigate("/main"); } });
위 코드는 사용자가 입력한 id, password를 담아 POST 방식으로 서버에 보냅니다.
받은 응답의 data.message에 따라 두 번째 then()에서 예외를 처리합니다.
- 간단 예제